TD CHOPs
# Basics
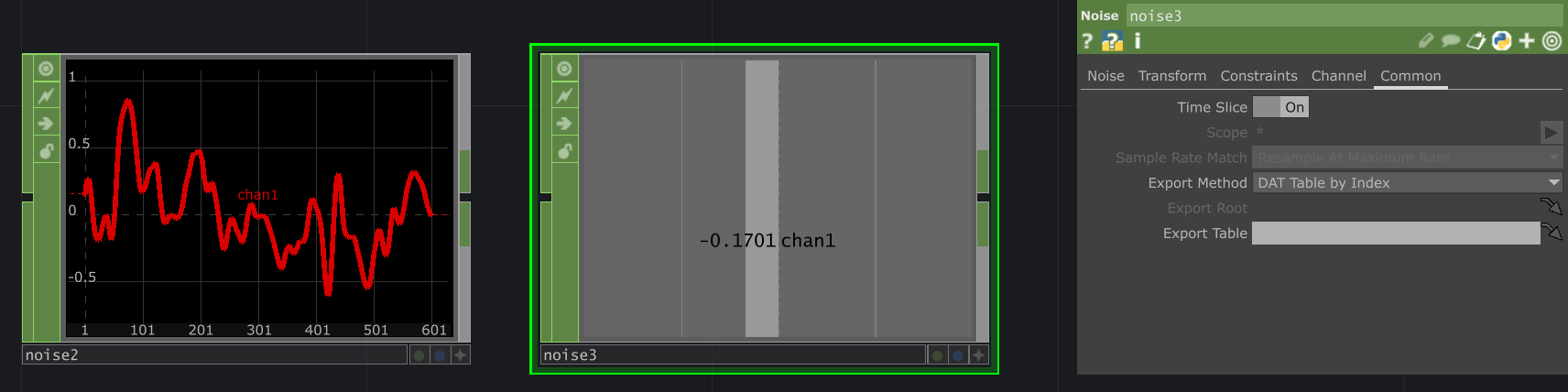
In the Common tab of every CHOP parameter panel you can enable Time Slice view. This displays the current values as a horizontal bar compared to a graph over time like the noise or trail CHOPs.
To reference CHOPs values in other operators you have to make the viewer on the CHOP you want to reference active and then drag and drop the viewer on the parameter you want to drive. Then select CHOP Reference.
In active viewer mode you can right click the viewer to reset the min/max bounds for better display
# CHOPs
# Constant
- create and name any floating point channels
# Noise
- generate different noise signals
- generate multiple noise channels in one CHOP by typing different channel names separated by commas in the channel parameter tab
# LFO
- generates different oscillator type signals (sine, triangle, ramp. etc.)
# Filter
- different filter and smoothing operations to work on the signal
# Trail
- trails the signal over time
# Math
- very powerful
- used to change range, multiply, offset etc.
# Logic
- useful to build 0,1 triggers: e.g. trigger if value is greater than x
# Limit
- clamp or quantize (step) values
# Select
- choose any number of existing CHOPs (rest gets discarded)
- wildcards work as expected
*selects everythingsomething*selects every channel that starts with something…
# Angle
- converts between different units (e.g. quaternion to degrees)
# Speed
- useful to add up values over time
# Trigger
- outputs 0 or 1 if threshold is reached
# Counter
- counts integer triggers
# Keyboard In
- let’s you specify keys and outputs 1 once pressed
# Mouse In
- output position, and button activations
- self explanatory
# Midi In
- Values often range from 0-127 (128 steps)
# Common Setups
# Normalize a Signal to 0-1
The 0-1 pulse signal from the LFO gets squeezed with the lag CHOP.
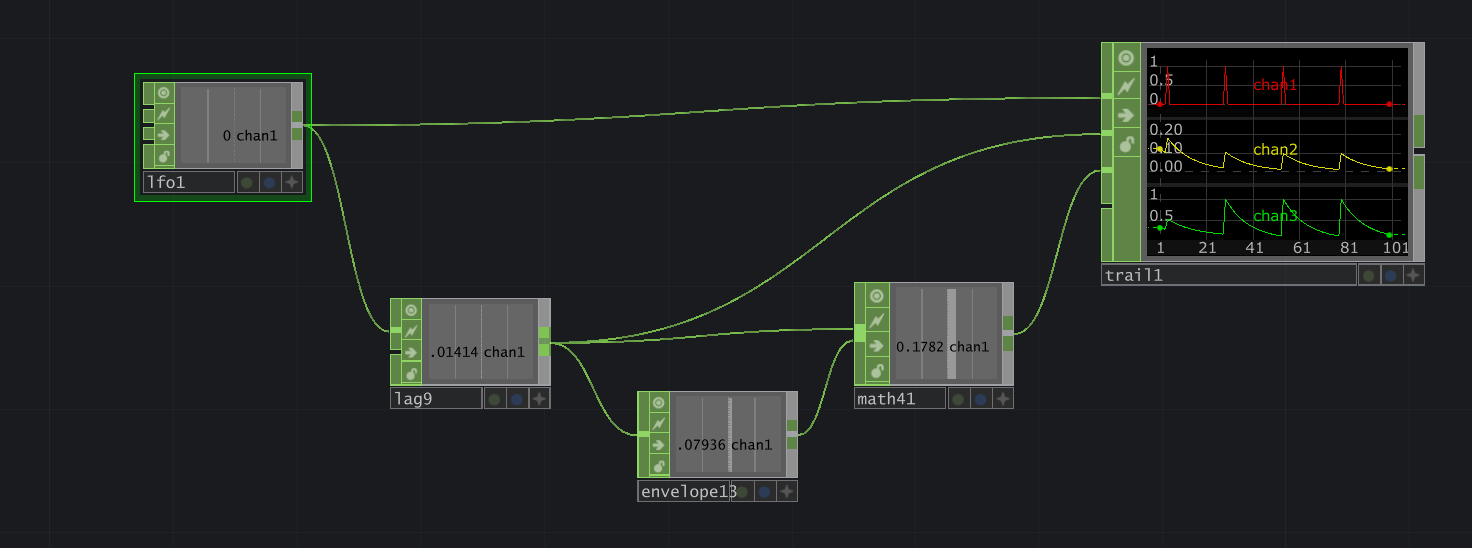
To normalize it again there is a neat trick using the envelope CHOP.
The Envelope CHOP outputs the maximum amplitude in the vicinity of each sample of the input.
Pretty much like Bounds over time in Houdini
Set it to a high number of seconds (e.g. 10). Just divide the signal through the output of it.