Vocabulary
# Buoyancy
All liquids and gases in the presence of gravity exert an upward force—called buoyancy—on any object immersed in them. If the object is less dense than the liquid or gas, buoyancy will make it float or rise upwards.
# Curl
Rotation of a vector field. Can be viewed as flow of fluid or gas through said field.
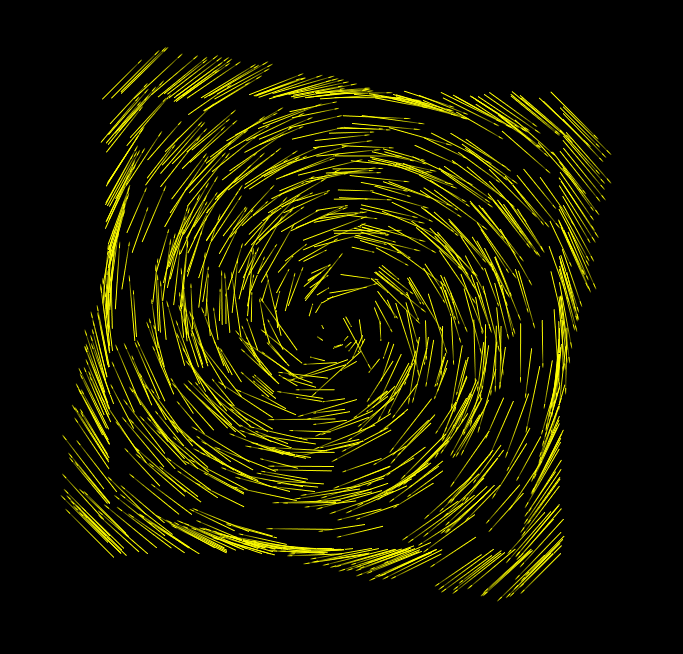
related to: Divergence
# Divergence
Flow of a vector field. Can be viewed as flow of fluid or gas through said field. Expanding Flow: positive Divergence (like a magnet pushing away) Compressing Flow: negative Divergence (like a magnet pulling in)
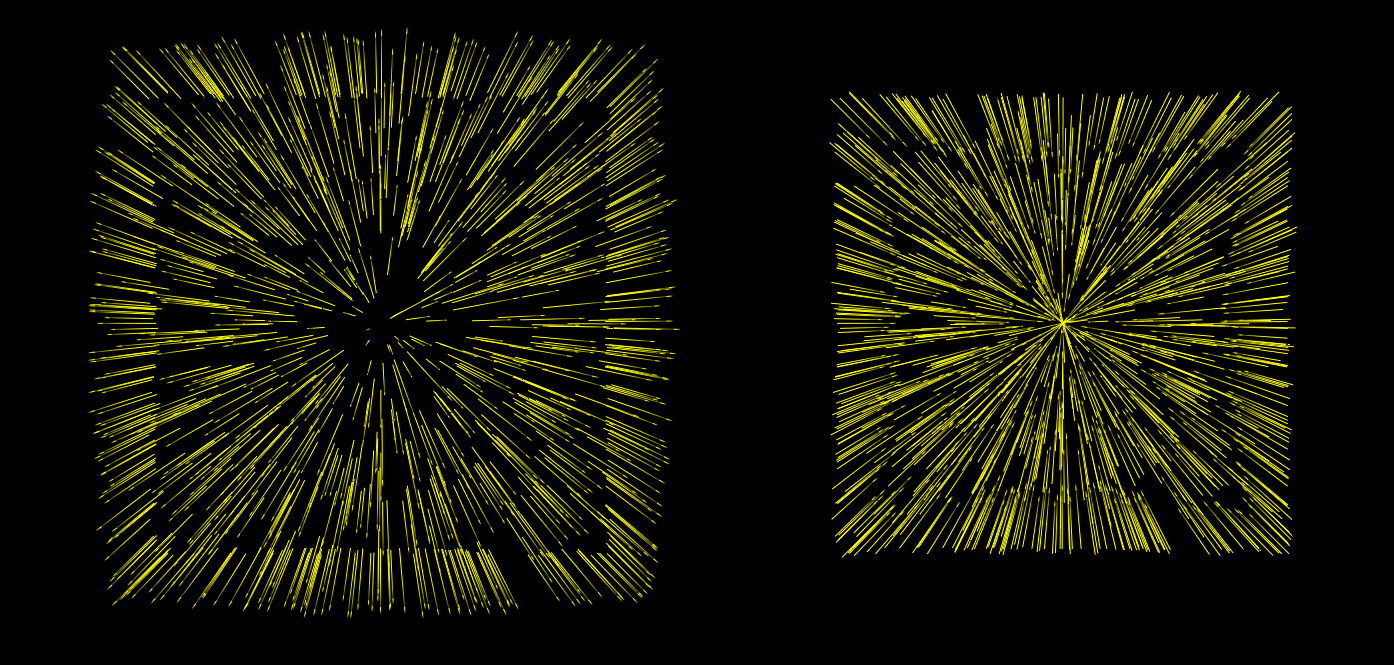
related to: Curl
# Eulerian Simulation
Values are stored on grids / volumes / fields think pyro simulation related to: Lagrangian Simulation
# Gradient
on volumes this can be used like normals on geometry to find out how the surface is oriented.
# Lagrangian Simulation
Values are stored on particles think POP simulation related to: Eulerian Simulation
# Scalar Fields
Scalar fields store a single float per voxel. Examples: Density, Temperature, Masks
# Vector Fields
Vector Fields store three floats per voxel. Examples: Color, Velocity, Force
# Vorticity
Vorticity is a pseudovector field that describes the local spinning motion of a continuum near some point (the tendency of something to rotate, as would be seen by an observer located at that point and traveling along with the flow.
# Perpendicular Lines
Lines that meet at right angle / 90 degrees
sources / further reading: